Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
The exact cause of PCOS is not clear. Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance. This means the body can't use insulin well. Insulin levels build up in the body and may cause higher androgen levels. Obesity can also increase insulin levels and make PCOS symptoms worse. PCOS may also run in families. It's common for sisters or a mother and daughter to have PCOS. The symptoms of PCOS vary.
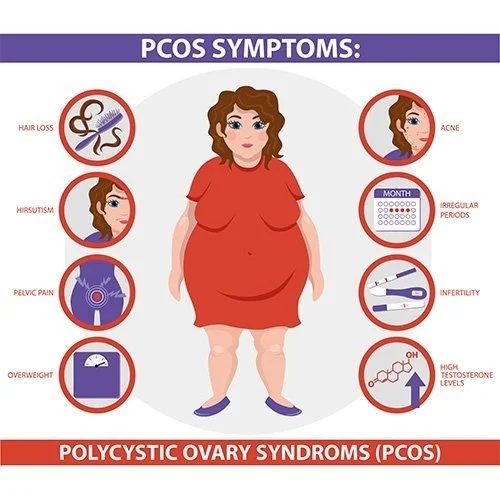
Symptoms
Facial/body hair
Increased weight
Hormonal acne
Irregular menstrual cycles
Infertility issues
Insulin resistance
Treatment
If you do plan to become pregnant, your treatment may include:
A change in diet and activity. A healthy diet and more physical activity can help you lose weight and reduce your symptoms. They can also help your body use insulin more efficiently, lower blood glucose levels, and may help you ovulate.
Medications to cause ovulation. Medications can help the ovaries to release eggs normally. These medications also have certain risks. They can increase the chance for a multiple birth (twins or more). And they can cause ovarian hyperstimulation. This is when the ovaries release too many hormones. It can cause symptoms such as abdominal bloating and pelvic pain.
If you do not plan to become pregnant, your treatment may include:
Birth control pills. These help to control menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and reduce acne.
Diabetes medication. This is often used to lower insulin resistance in PCOS. It may also help reduce androgen levels, slow hair growth, and help you ovulate more regularly.
A change in diet and activity. A healthy diet and more physical activity can help you lose weight and reduce your symptoms. They can also help your body use insulin more efficiently, lower blood glucose levels, and may help you ovulate.
Medications to treat other symptoms. Some medications can help reduce hair growth or acne.